Find a sample of our customers applications.
We have a lot more to share with you. Please tell us about your research field and we will prepare a selection for you.
Oncology
Biospace Lab contributes to the great efforts devoted to cancer research, which represents a major concern for human health.
- Concurrently visualize and discriminate the primary tumor and metastases thanks to our dynamic acquisition technology.
- Monitor progression of a continuously evolving disease and follow the effects of potential treatments with longitudinal studies.
- Detect micro-metastasis from very early stages.
- Accurately quantify tumor-related signals within specific anatomical contexts, even for deep tissues usually tricky to visualize.
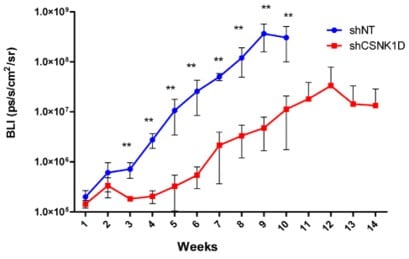
Bar, I. et al. Silencing of casein kinase 1 delta reduces migration and metastasis of
triple negative breast cancer cells. Oncotarget (2018)
Non-targeted (control)
The primary tumor grows over time in triple negative breast cancer xenografts
Silencing of CSNK1D
CSNK1D knock-down slows down tumor development
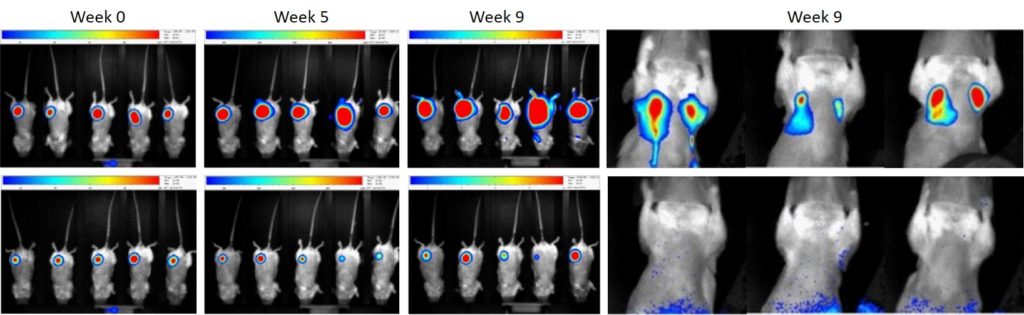
CSNK1D knock-down prevents metastasis formation, while lung metastases develop in shNT triple negative breast cancer xenografts
The highly dynamic range of the camera
allows to follow-up the primary tumor
as well as to detect lung metastases.
Bar, I. et al. Silencing of casein kinase 1 delta reduces migration and metastasis of
triple negative breast cancer cells. Oncotarget (2018)
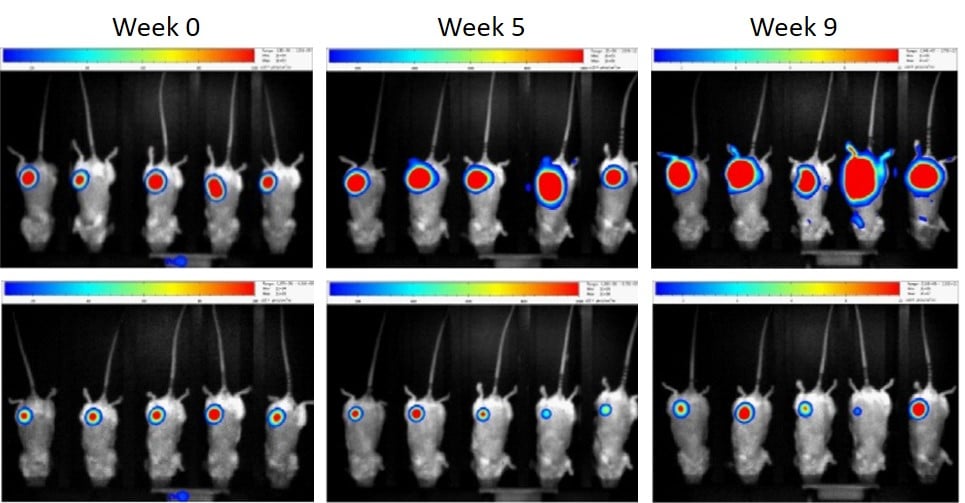
1st line: Non-targeted (control)
The primary tumor grows over time in triple negative breast cancer xenografts
2nd line Silencing of CSNK1D
CSNK1D knock-down slows down tumor development

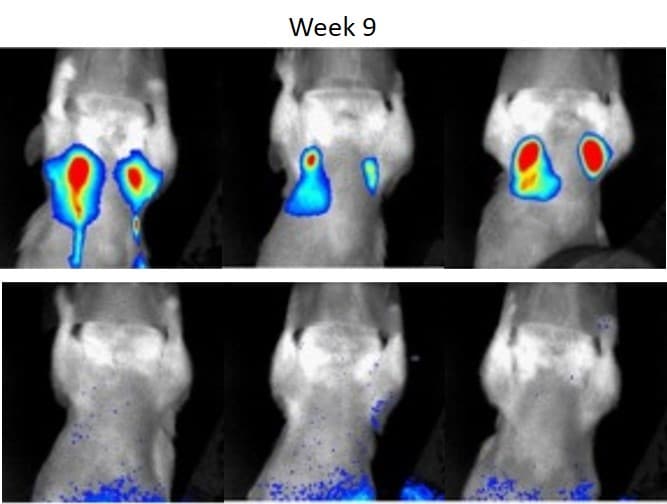
CSNK1D knock-down prevents metastasis formation, while lung metastases develop in shNT triple negative breast cancer xenografts
The highly dynamic range of the camera allows to follow-up the primary tumor as well as to detect lung metastases.
Jarry, U. et al. Orthotopic model of lung cancer: isolation of bone micro-metastases
after tumor escape from Osimertinib treatment. BMC Cancer (2021)
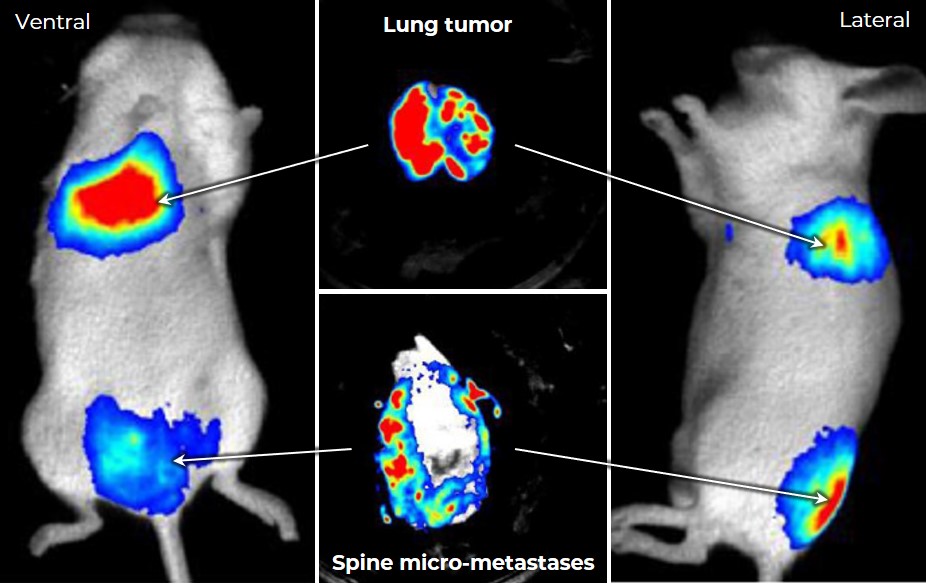
Orthotopic model of lung cancer:
– lung primary tumor nesting
– metastases dissemination after Osimertinib treatment
Bone micro-metastases were easily detected using bioluminescence, allowing isolation of tumor cells otherwise undetectable by macroscopic observation.
Germanova, D. et al. Myeloid tumor necrosis factor and heme oxygenase‐1 regulate the progression of colorectal liver metastases during hepatic ischemia‐reperfusion. International Journal of Cancer (2021)
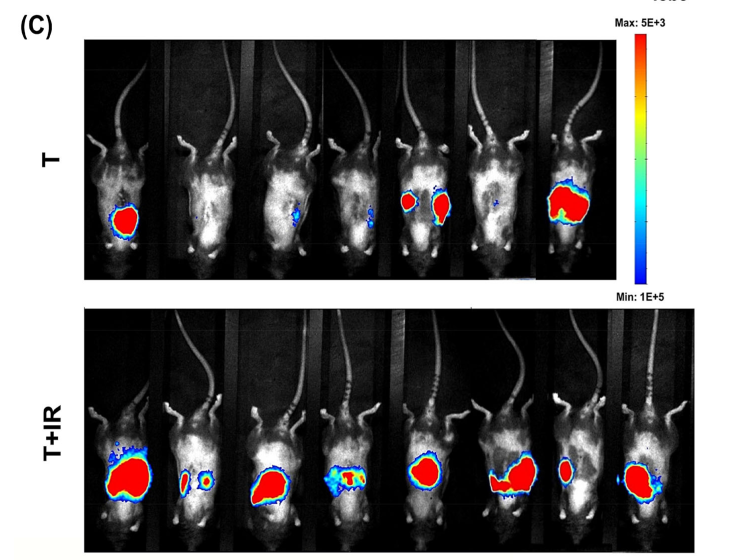
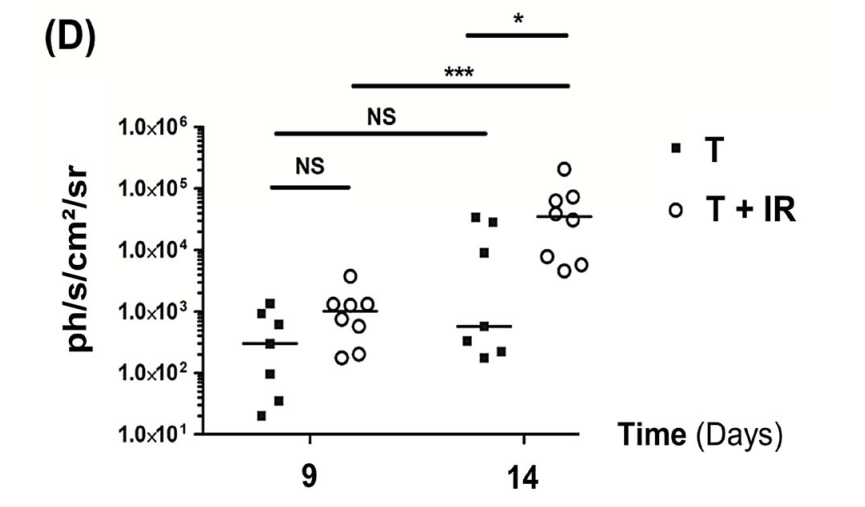
Bogeas, A. et al. Changes in chromatin state reveal ARNT2 at a node of a tumorigenic transcription factor signature driving glioblastoma cell aggressiveness. Acta Neuropathologica (2018)
shCTL (control)
Mice with
orthotopic xenograft of glioblastoma
stem-like cells (left) almost inevitabely develop a tumor
Silencing of ARNT2
ARNT2 knock-down (right) strikingly reduce tumor incidence in mice grafted with glioblastoma
stem-like cells
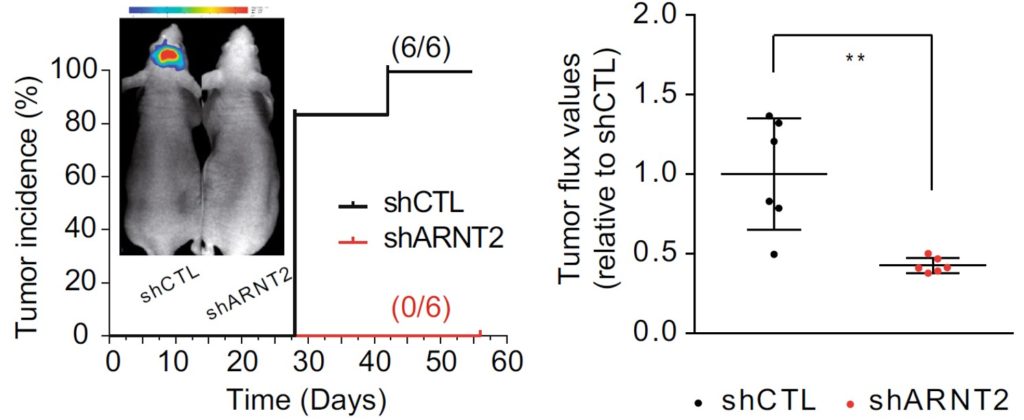
Longitudinal analysis of bioluminescence allows to reveal tumor incidence and the timing of its occurrence.
Bogeas, A. et al. Changes in chromatin state reveal ARNT2 at a node of a tumorigenic transcription factor signature driving glioblastoma cell aggressiveness. Acta Neuropathologica (2018)

shCTL (control)
Mice with orthotopic xenograft of glioblastoma stem-like cells (left) almost inevitabely develop a tumor
shARNT2: Silencing of ARNT2
ARNT2 knock-down (right) strikingly reduce tumor incidence in mice grafted with glioblastoma stem-like cells
Longitudinal analysis of bioluminescence allows to reveal tumor incidence and the timing of its occurrence.
Arfaoui, A. et al. A genome‐wide RNAi screen reveals essential therapeutic targets of breast cancer stem cells. EMBO Molecular Medicine (2019)
Untreated (control)
Primary breast cancer xenografts engender liver and lung metastasis formation in untreated mice
Salinomycin treated
Salinomycin alone does not significantly impair metastasis development
JQ1 treated
JQ1 alone does not significantly impair metastasis development
Salinomycin/ JQ1 treated
The salinomycin/JQ1 combination is efficent for significant reduction of metastasis formation
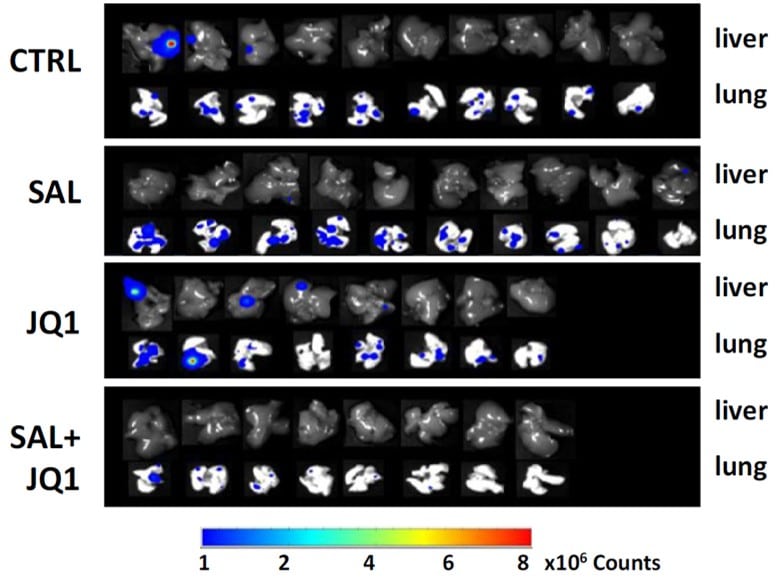
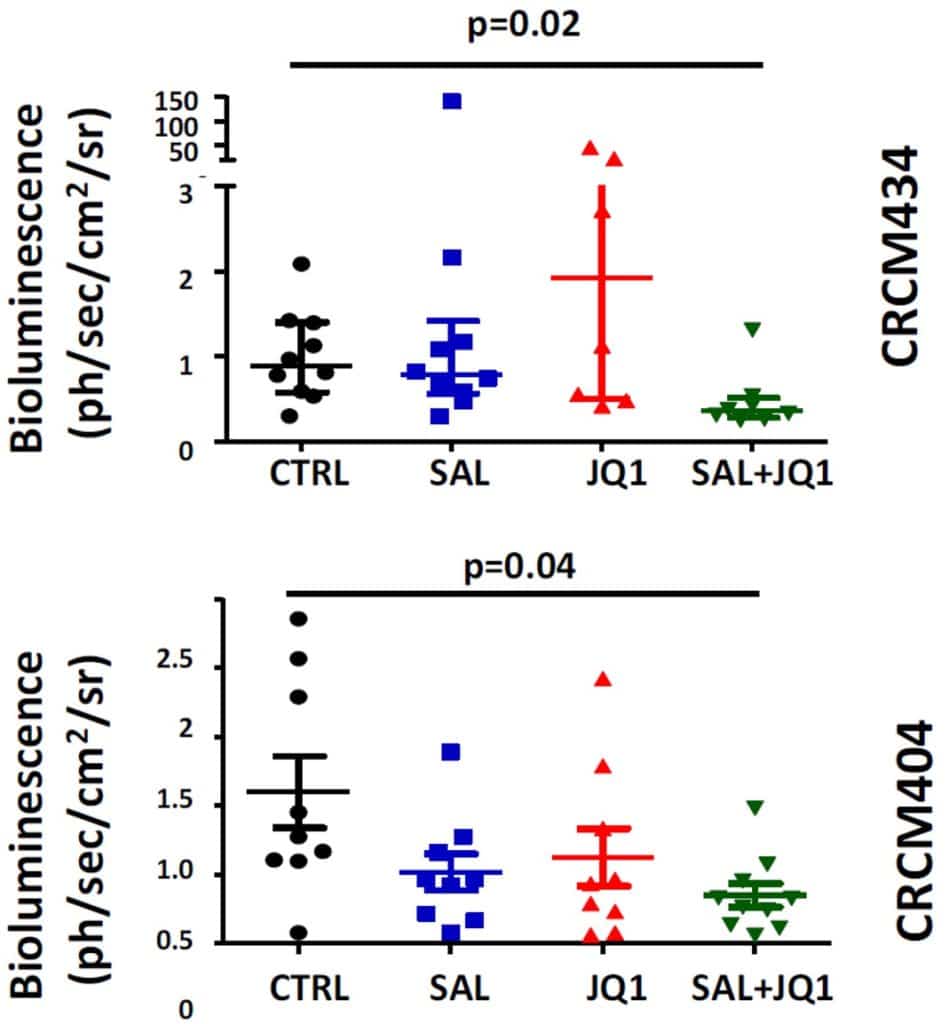
Treatment efficacy on metastasis development is quantified in two primary human breast cancer xenograft models (CRCM434 and 404), generated from patients with chemo-naïve triple-negative breast tumors.
Drug combination assay and ex vivo imaging display the synergistic interaction of salinomycin/JQ1 association to limit breast cancer metastatic development.
Arfaoui, A. et al. A genome‐wide RNAi screen reveals essential therapeutic targets of breast cancer stem cells. EMBO Molecular Medicine (2019)

CTRL: Untreated (control)
Primary breast cancer xenografts engender liver and lung metastasis formation in untreated mice
SAL: Salinomycin treated
Salinomycin alone does not significantly impair metastasis development
JQ1: JQ1 treated
JQ1 alone does not significantly impair metastasis development
SAL+JQ1: Salinomycin/ JQ1 treated
The salinomycin/JQ1 combination is efficent for significant reduction of metastasis formation

Treatment efficacy on metastasis development is quantified in two primary human breast cancer xenograft models (CRCM434 and 404), generated from patients with chemo-naïve triple-negative breast tumors.
Drug combination assay and ex vivo imaging display the synergistic interaction of salinomycin/JQ1 association to limit breast cancer metastatic development.
Neuroscience
The central nervous system is a complex and fascinating structure that remains yet complicated to image. Biospace Lab supports neurobiologists in this challenge.
- Observe the brain and detect signals of interest from its distinct regions in vivo through the intact skull of the animal.
- Avoid anesthesia-related bias and open exciting avenues for behavioral studies by working on non-anesthetized animals.
- Employ Ca2+ reporters to reveal oscillations in Ca2+ concentration and thus measure neuronal activity.
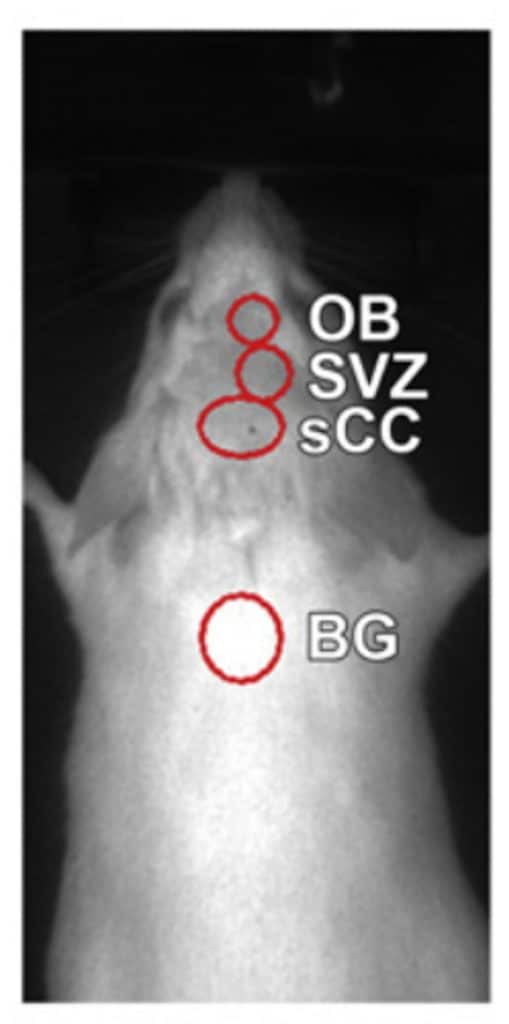
Guglielmetti, C. Prael, J. et al. Multimodal imaging of subventricular zone neural stem/progenitor cells in the cuprizone mouse model reveals increased neurogenic potential for the olfactory bulb pathway, but no contribution to remyelination of the corpus callosum. NeuroImage (2014)
Untreated (control)
In situ labeled NPCs of the subventricular zone (SVZ) migrate towards the olfactory bulb (OB)
Multiple sclerosis model
Significantly increased migration of NPCs from the SVZ to the OB is evidenced in cuprizone-treated mice
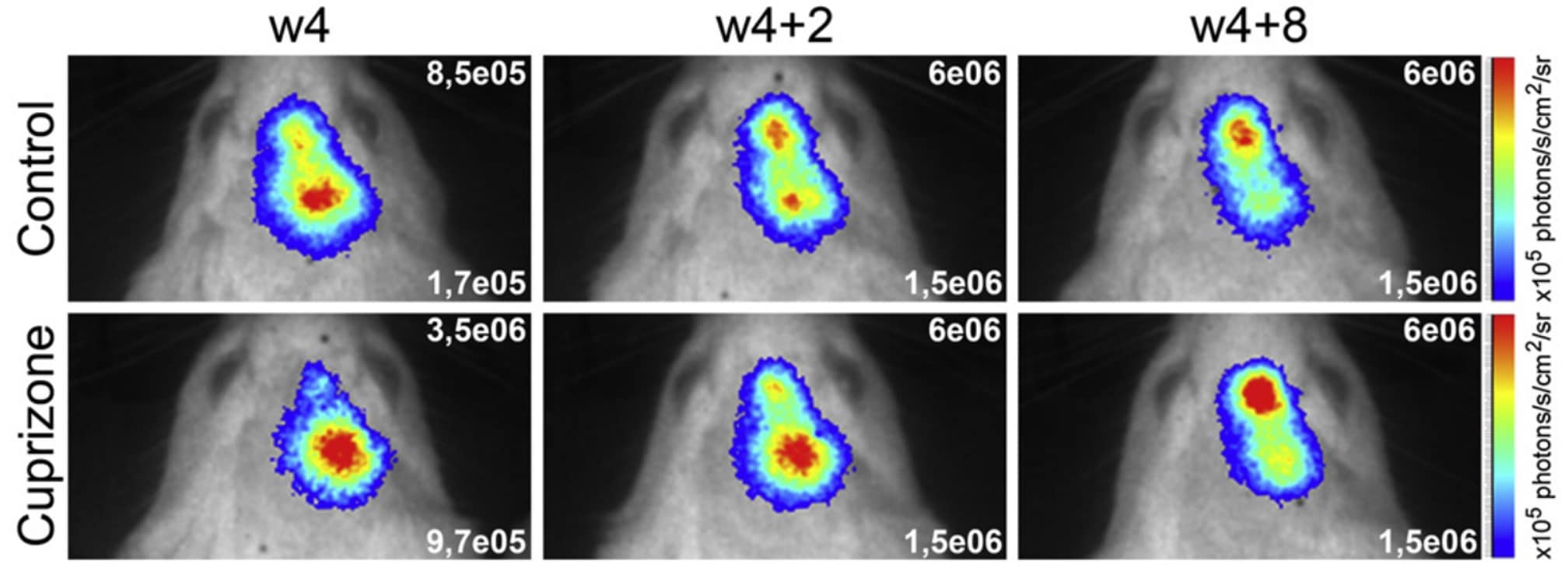
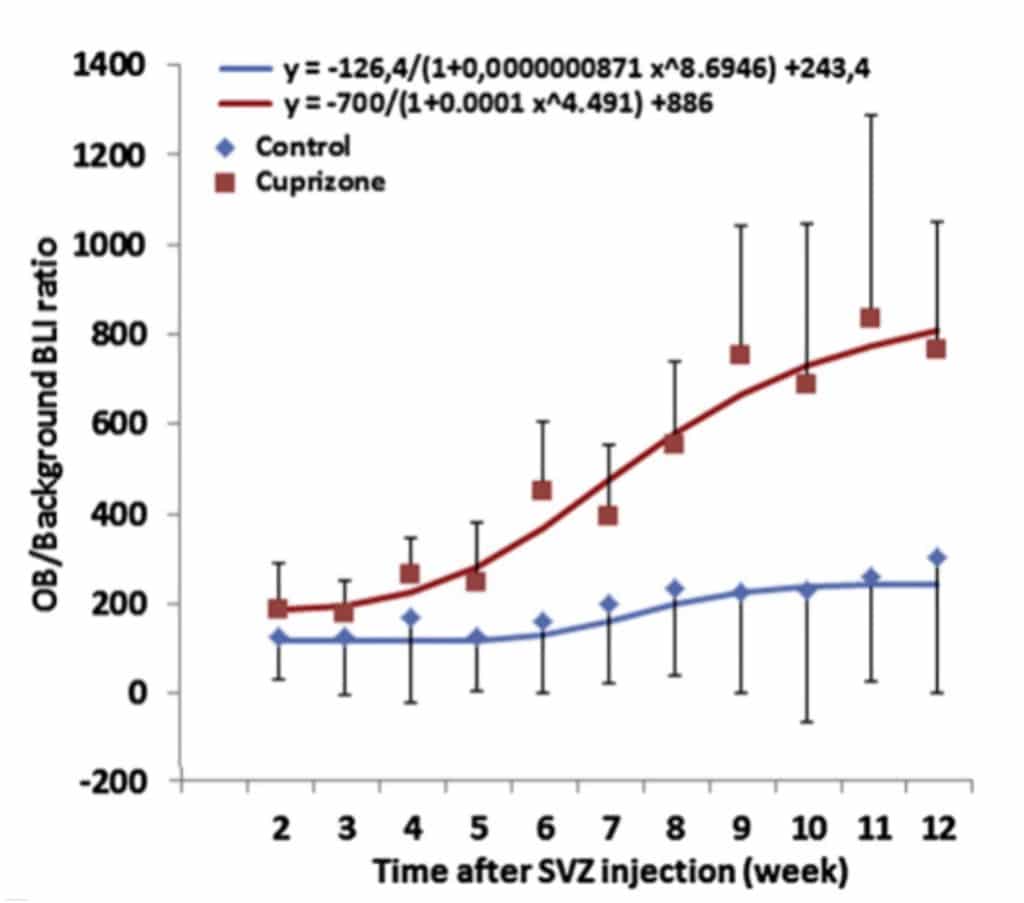
Longitudinal in vivo tracking allows
monitoring neural progenitor cells (NPCs)
within distinct brain regions.
Increased proliferation and significant alteration of NPC migration from the SVZ to the OB has been highlighted in a murine model of multiple sclerosis, induced by cuprizone treatement.
Guglielmetti, C. Prael, J. et al. Multimodal imaging of subventricular zone neural stem/progenitor cells in the cuprizone mouse model reveals increased neurogenic potential for the olfactory bulb pathway, but no contribution to remyelination of the corpus callosum. NeuroImage (2014)

Untreated (control)
In situ labeled NPCs of the subventricular zone (SVZ) migrate towards the olfactory bulb (OB)
Cuprizone: Multiple sclerosis model
Significantly increased migration of NPCs from the SVZ to the OB is evidenced in cuprizone-treated mice

Longitudinal in vivo tracking
allows monitoring neural
progenitor cells (NPCs)
within distinct brain regions.
Increased proliferation and significant alteration of NPC migration from the SVZ to the OB has been highlighted in a murine model of multiple sclerosis, induced by cuprizone treatement.

Gakuba, C. et al. General anesthesia inhibits the activity of the “glymphatic system”. Theranostics (2018)
Awake
The indocyanine green fluorescent tracer injected into the cisterna magna (orange) diffuses through the brain and is readily detectable in the forebrain (red)
Anesthetized (isoflurane)
The intracisternally injected indocyanine green remains near the injection site in the anesthetized mice
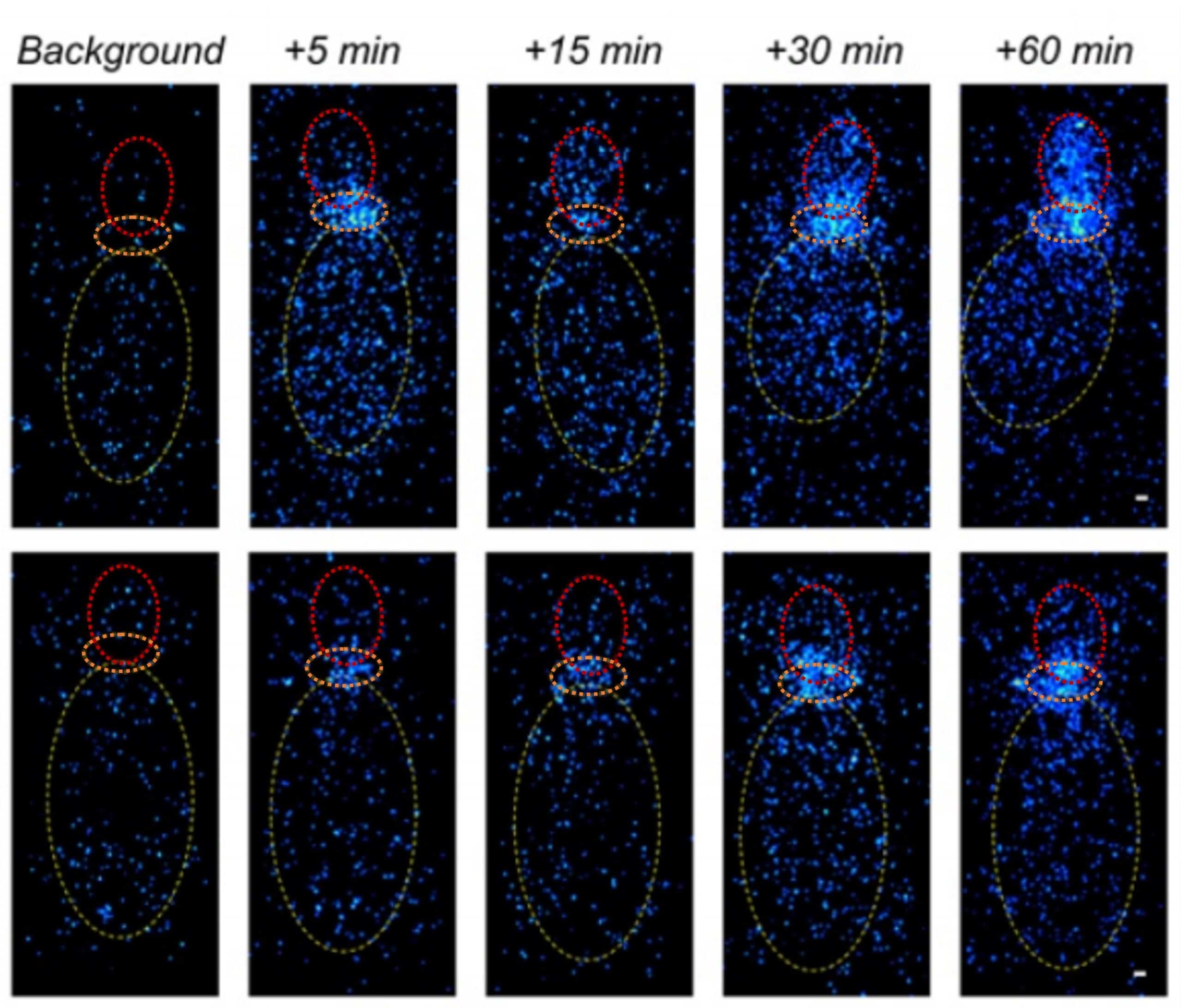
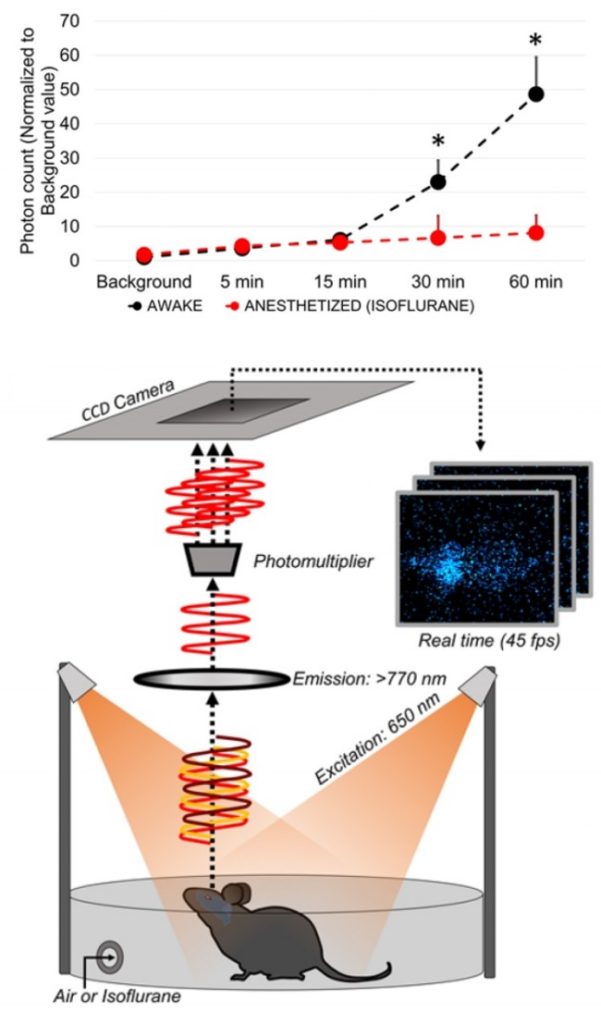
As soon as 30 min after intracisternal injection, the amount of indocyanine green in the forebrain of awake mice is significantly higher with respect to anesthetized mice.
Longitudinal in vivo near infrared imaging of freely moving mice revealed that cerebrospinal fluid flow circulation is mainly active during wakefulness
and significantly impaired during
general anesthesia.
Gakuba, C. et al. General anesthesia inhibits the activity of the “glymphatic system”. Theranostics (2018)
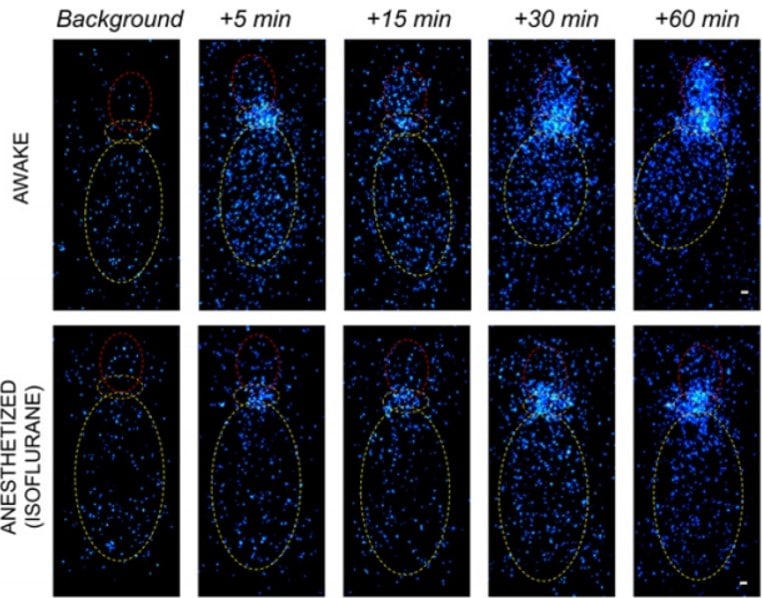
Awake
The indocyanine green fluorescent tracer injected into the cisterna magna (orange) diffuses through the brain and is readily detectable in the forebrain (red)
Anesthetized (isoflurane)
The intracisternally injected indocyanine green remains near the injection site in the anesthetized mice
As soon as 30 min after intracisternal injection, the amount of indocyanine green in the forebrain of awake mice is significantly higher with respect to anesthetized mice.

Longitudinal in vivo near infrared imaging of freely moving mice revealed that cerebrospinal fluid flow circulation is mainly active during wakefulness and significantly impaired during general anesthesia.
Rogers, K. L. et al. Non-Invasive In Vivo Imaging of Calcium Signaling in Mice. PLoS ONE (2007)
Seizure induced by kainate administration in non-anesthetized mice, provokes highly synchronized, bi-lateral Ca2+ transients.
This increased Ca2+ activity is measured using GFP-aequorin as a bioluminescent Ca2+-reporter.
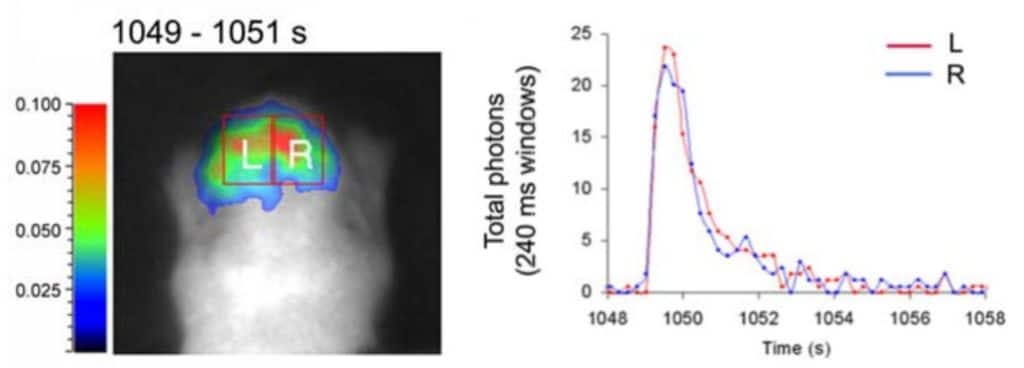
Real-time bioluminescent signal acquisition allows to detects
rapid Ca2+ transients.
A marked increase in Ca2+ activity occurred approximately 15 minutes after drug administration.
This phenomenon is evidenced as oscillations in which Ca2+ spikes only last a few seconds.
Stem Cell Biology
Stem cells are essential actors in embryonic development, and tissue homeostasis and renewal. Biospace Lab provides versatile solutions that offer decisive advantages for investigating and exploiting the exclusive potential of stem cells.
- Track stem cells in space and time with relevant lineage reporters.
- Monitor cell fate by observing migration and maturation events leading to differentiation.
- Estimate crucial cellular processes such as cell proliferation, survival and apoptosis.
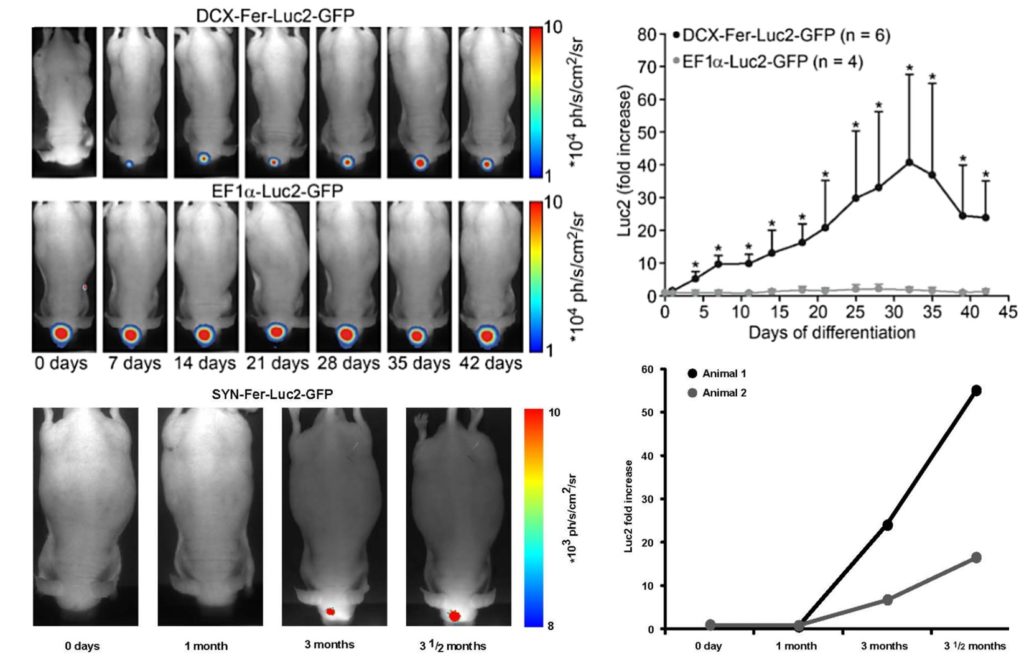
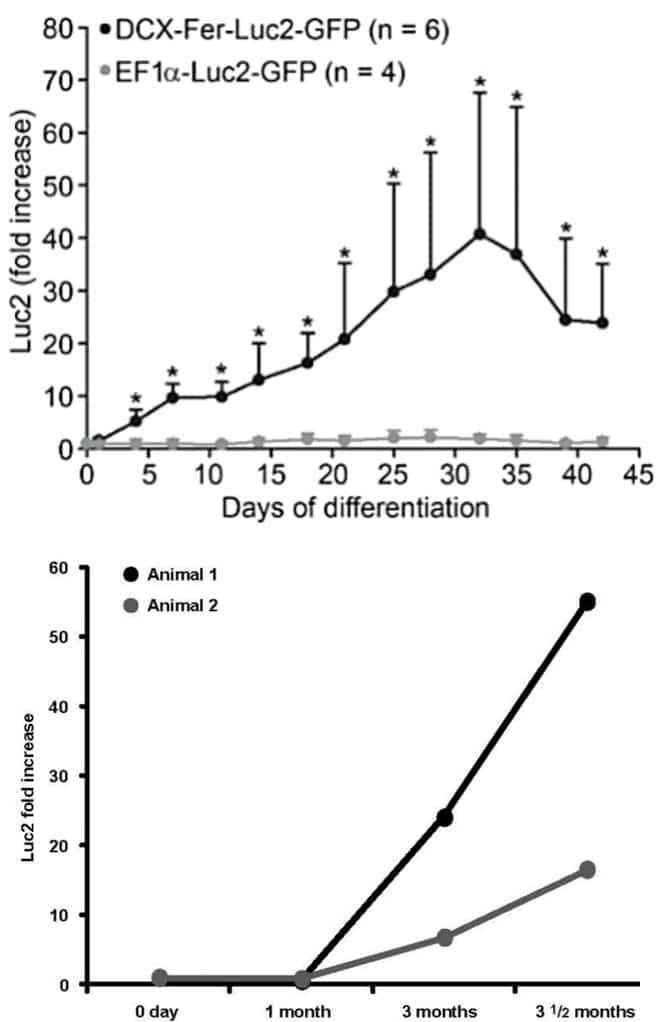
Tennstaedt, A. et al. Human neural stem cell intracerebral grafts show spontaneous early neuronal differentiation after several weeks. Biomaterials (2015)
Early neuronal reporter
Newly born neuron signal increases within the first month after NSC implantation
Constitutively expressed reporter (control)
The signal remains stable over time
Mature neuronal reporter
Ongoing maturation of neurons and synaptogenesis is detectable from 3 months post-implantation
Tennstaedt, A. et al. Human neural stem cell intracerebral grafts show spontaneous early neuronal differentiation after several weeks. Biomaterials (2015)
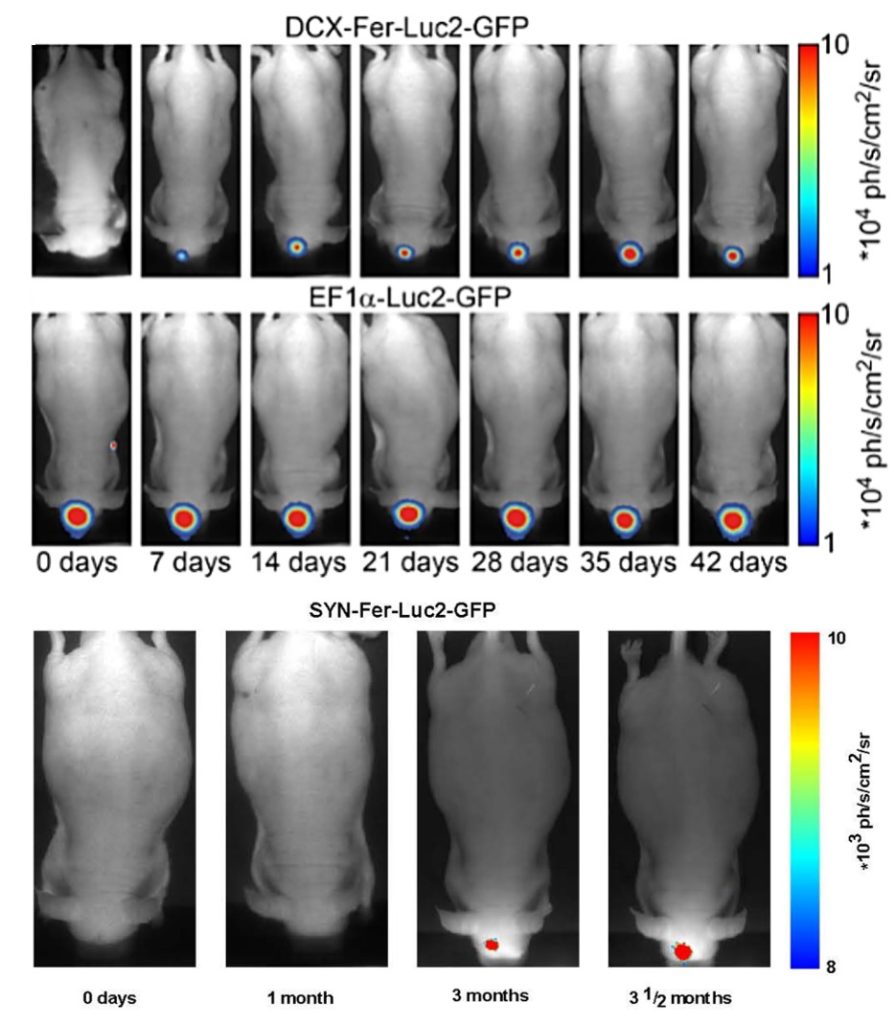
1st line: Early neuronal reporter
Newly born neuron signal increases within the first month after NSC implantation
2nd line: Constitutively expressed reporter (control)
The signal remains stable over time
3rd line: Mature neuronal reporter
Ongoing maturation of neurons and synaptogenesis is detectable from 3 months post-implantation
Virology / Infectious Diseases
- In order to accommodate all your virology studies, our systems can help you visualize and track cell infection in real time as from the very first second and even with very low level of virus.
- Our systems are designed to be installed and maintained in BSL-2 or BSL-3 laboratories.
Pavlidis, I. et al. Cervical epithelial damage promotes Ureaplasma parvum ascending infection, intrauterine inflammation and preterm birth induction in mice. Nature Communications (2020)
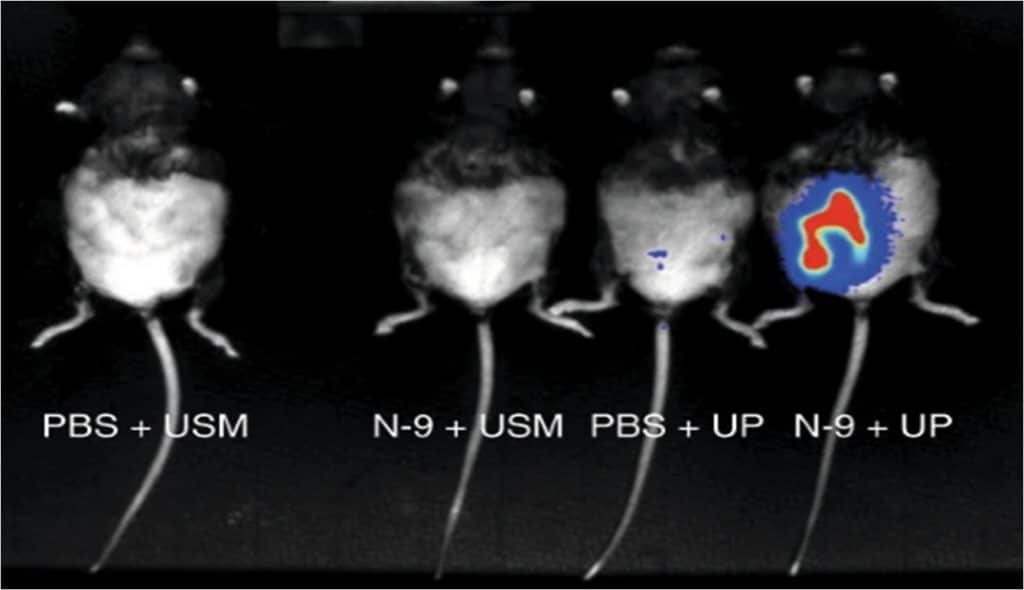
Controls
No signal is detectable in untreated (PBS) or in N-9 treated mice when not subjected to infection (USM)
Untreated
Low bacterial load is observable in untreated mice infected with a luciferase-expressing Ureaplasma parvum strain (UP)
N-9 induced cervical damage
Intravaginal exposure to N-9 facilitates intrauterine UP infection
Bioluminescent bacteria emanate
high-intensity signals with the expected
shape and location of the uterus, showing bulges representing gestating foetus
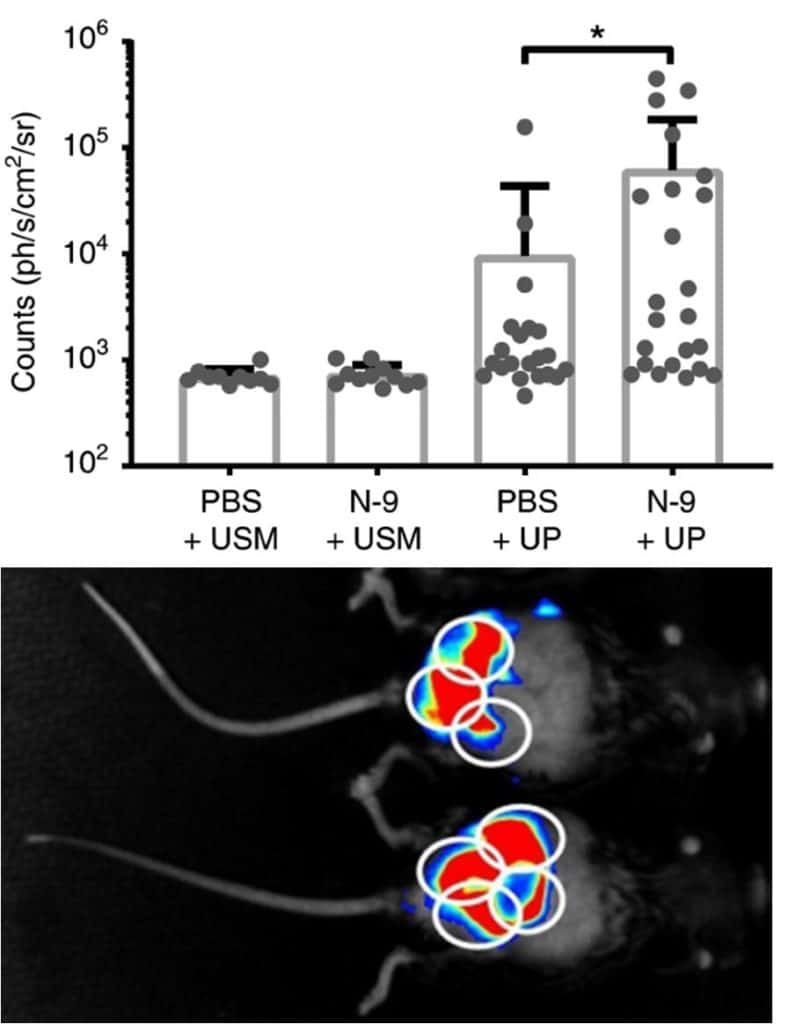
In vivo imaging allows to visualize the ascending
Ureaplasma parvum infection in pregnancy,
demonstrating the crucial role of the cervical epithelium
as a barrier against ascending infection and preterm birth.
Pavlidis, I. et al. Cervical epithelial damage promotes Ureaplasma parvum ascending infection, intrauterine inflammation and preterm birth induction in mice. Nature Communications (2020)

Controls
No signal is detectable in untreated (PBS) or in N-9 treated mice when not subjected to infection (USM)
Untreated
Low bacterial load is observable in untreated mice infected with a luciferase-expressing Ureaplasma parvum strain (UP)
N-9 induced cervical damage
Intravaginal exposure to N-9 facilitates intrauterine UP infection

Bioluminescent bacteria emanate
high-intensity signals with the expected shape and location of the uterus, showing bulges representing gestating foetuses
In vivo imaging allows to visualize the ascending Ureaplasma parvum infection in pregnancy, demonstrating the crucial role of the cervical epithelium as a barrier againstascending infection and preterm birth.
Raaben, M. et al. Non-invasive imaging of mouse hepatitis coronavirus infection reveals determinants of viral replication and spread in vivo. Cellular Microbiology (2009)
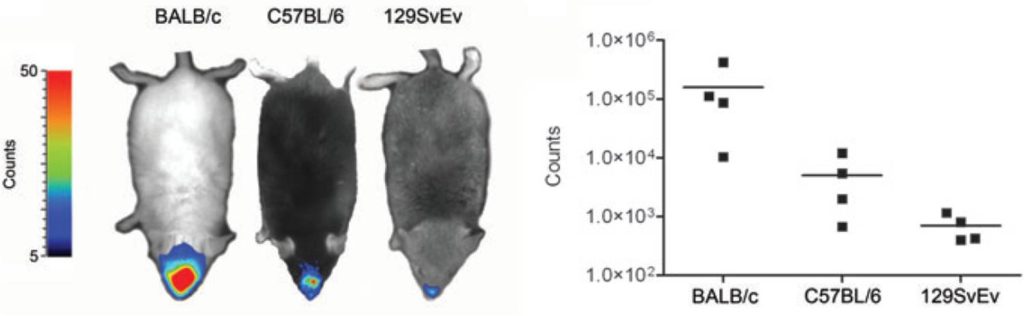
Mice with different genetic background have been intranasally inoculated with
lucifesare-expressing mouse hepatitis virus (MHV)
BALB/c mouse strain
BALB/c mice display the highest luminescent signal
C57BL/6 mouse strain
C57BL/6 mice have an intermediate phenotype compared to the other genetic backgrounds
129SvEv mouse strain
129SvEv mice are significantly less susceptible to MHV infection
Non-invasive whole-body imaging of viral infection
in living animals allows to monitor its spatial
and temporal progression in real-time.
Follow-up of viral replication can be performed
in parallel for different animals, here unveiling
the variable susceptibility of various
inbred mouse strains to MHV infections.
Weinmann, J. et al. Identification of a myotropic AAV by massively parallel in vivo evaluation of barcoded capsid variants. Nature Communications (2020)
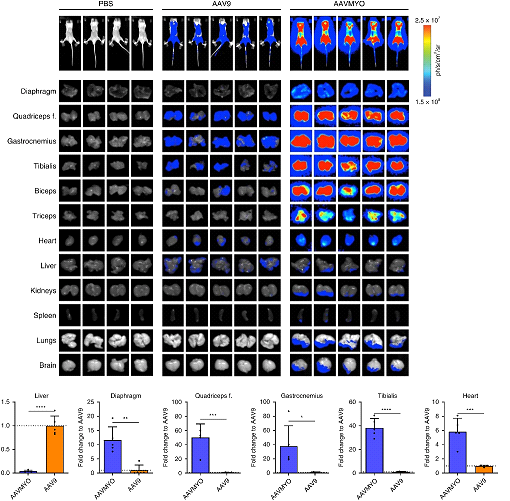
Pharmacology / biodistribution
- Visualize small area of interests in the brain or other organs with excellent spatial resolution.
- Visualize the anatomical distribution of a protein of interest in tissues, and know the drug distribution.
- Quantify radioisotope-labelled substances in tissue sections, in binding or In Situ Hybridization (ISH) experiments.
- Follow the dose effect quantifications in your pharmacological experiments, such as with radio-labelled ligand displacement studies.
- Control your PET or SPECT experiments in preclinical nuclear medicine studies.
- Improve your experiment understanding: simultaneous imaging of distribution and quantification of three different radiolabeled markers in histopathologic slices. Simultaneous observation of 3 different processes: metabolism, perfusion and interstitial fluid in organ of interest.
Zinnhardt, B. et al. Molecular imaging of immune cell dynamics during de- and remyelination in the cuprizone model of multiple sclerosis by [18F]DPA-714 PET and MRI. Theranostics (2019)
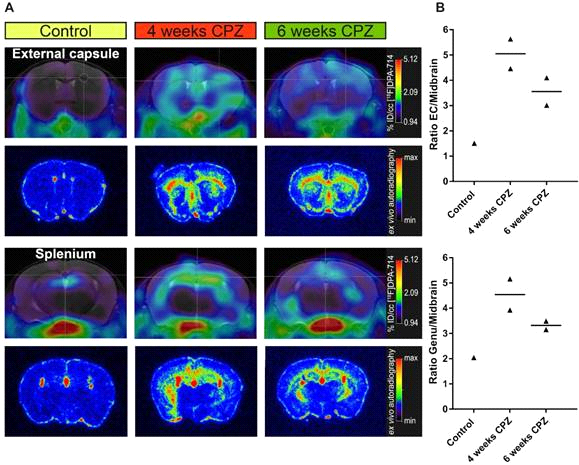
Comparison of in vivo PET data with ex vivo autoradiography. (A) Ex vivo autoradiography confirms the in vivo spatial distribution of [18F]DPA-714 (n = 1-2).
Kryza, D. et al. Ex vivo and in vivo imaging and biodistribution of aptamers targeting the human Matrix MetalloProtease-9 in melanomas. PLoS ONE (2016)
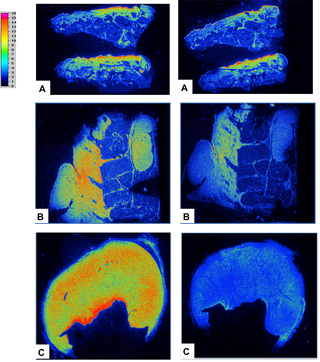
Comparison of the results obtained by radiolabeling of representative tumor tissue sections with 111In-DOTA-F3B aptamer (left image) and 111In-DOTA-control sequence (right image).The difference of activity seems to increase in a tumor grade-dependent manner. (A) Lentigo malignant melanoma, (B) Nodular melanoma, (C) Mostly metastatic node.
Alitalo, O., Rantamäki, T. & Huhtala, T. Digital autoradiography for efficient functional imaging without anesthesia in experimental animals: Reversing phencyclidine-induced functional alterations using clozapine. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry (2020)
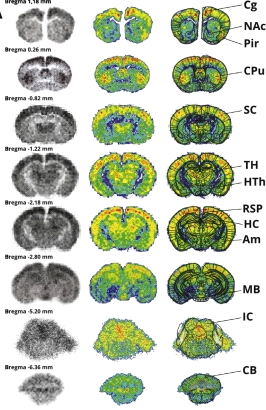
“With the advances in direct particle-counting systems, the new digital ARG devices have surpassed the conventional film and phosphor screen-based ARG in linearity, dynamic range, and sensitivity, reducing the acquisition times from months to just few hours.”
“An example of qualitative results acquired from control group with BetaImager TRacer using 3H-labeled 2-deoxy-d-glucose as a tracer. The acquisition was performed for 6 h on a full-field zoom setting (250 × 200 mm) »
Alitalo, O., Rantamäki, T. & Huhtala, T. Digital autoradiography for efficient functional imaging without anesthesia in experimental animals: Reversing phencyclidine-induced functional alterations using clozapine. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry (2020)

“With the advances in direct particle-counting systems, the new digital ARG devices have surpassed the conventional film and phosphor screen-based ARG in linearity, dynamic range, and sensitivity, reducing the acquisition times from months to just few hours.”
“An example of qualitative results acquired from control group with BetaImager TRacer using 3H-labeled 2-deoxy-d-glucose as a tracer. The acquisition was performed for 6 h on a full-field zoom setting (250 × 200 mm) »
Other Applications
Virtually any beta emitting radioisotope with sufficient energy will generate Cerenkov luminescence in vivo , including those for which no current in vivo imaging solutions exist; such as 32P, 90Y and 90Sr.

2.5 μCi of 90Y radiotracer concentrated in the pancreas of a mouse—imaged with PhotonIMAGER
Cerenkov luminescence with the 4-View module of the PhotonIMAGER™
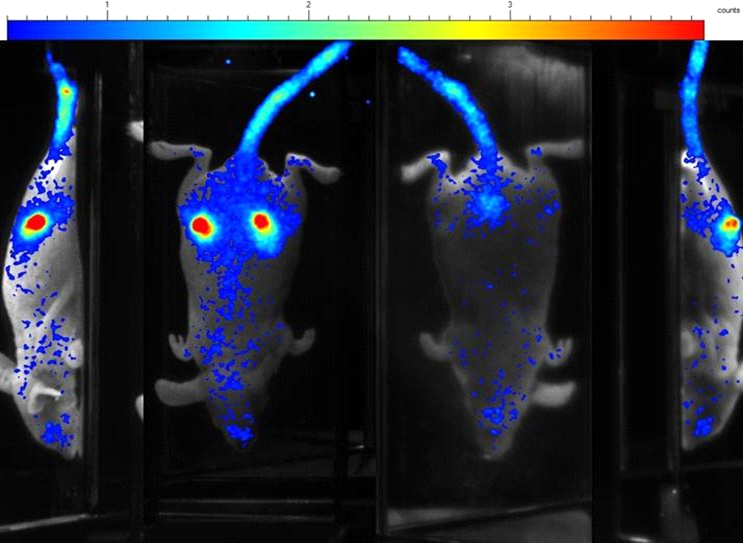
Images of a mouse from 4 different angles 4h after the injection of 50 μCi 32P. Cerenkov luminescence signal appears in subcutaneous tumor — with a high pass (530nm) filter.
